🕒 The Hidden Clock in Your Stomach: A Complete Guide to Food Digestion Times and Smarter Eating
Ever wonder why you feel light and energized after a fruit smoothie but need a nap after a heavy lunch? The answer lies in how long your stomach spends digesting different types of food. Food doesn’t just disappear when we eat it—it embarks on a carefully timed journey through the digestive system.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the science behind digestion time, break down common foods from fastest to slowest, and show you how to use this knowledge to improve your energy levels, gut health, and even your mood. Plus, we’ll share expert insights, practical meal plans, and smart pairing suggestions to help you make digestion-friendly choices without sacrificing flavor or joy.
🌱 Chapter 1: What Is Digestion Time and Why Does It Matter?
Digestion time refers to how long it takes your stomach to break down food and pass it to the small intestine. It can range from a few minutes to several hours depending on the type, density, and composition of what you eat.
Why It Matters:
- Prevents Bloating and Discomfort: Mixing fast and slow-digesting foods can lead to fermentation in the stomach, producing gas, indigestion, or sluggishness.
- Boosts Energy Efficiency: Knowing which foods fuel your body quickly versus those that keep you full longer helps you time meals for productivity or workouts.
- Improves Nutrient Absorption: Giving your stomach the right pace ensures it doesn’t become overloaded, allowing optimal breakdown and nutrient delivery.
- Supports Weight Balance and Gut Health: Strategic meal planning around digestion can stabilize blood sugar levels, reduce overeating, and minimize stress on the gut.
🧪 Chapter 2: How Digestion Works—From Bite to Fuel
Here’s a simplified breakdown of what happens when you eat:
- Mouth (1–2 minutes): Chewing breaks down food mechanically and enzymes in saliva begin carbohydrate digestion.
- Stomach (30 minutes to 6+ hours): Gastric acid and enzymes break down proteins and emulsify fats. This is where digestion time varies most.
- Small Intestine (3–6 hours): Nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream.
- Large Intestine (12–48 hours): Water and salts are absorbed; fiber is fermented by gut bacteria.
Your stomach doesn’t digest all foods equally—fruits fly through like express trains, while nuts take their sweet time. Let’s break it down.
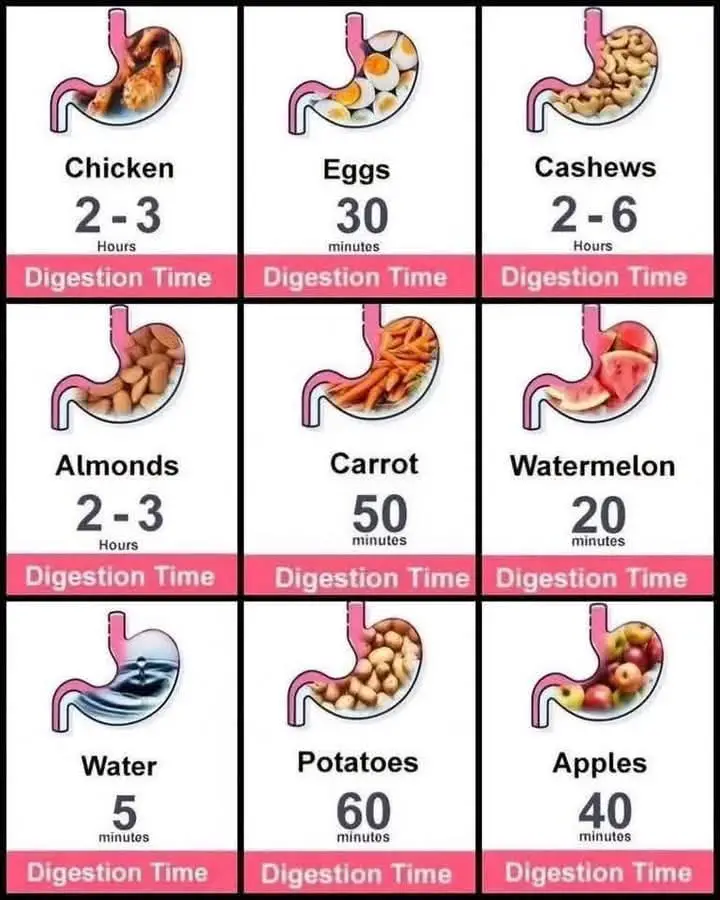
🥗 Chapter 3: Foods by Digestion Time
Below is a categorized guide to the digestion times of common foods, based on an average healthy adult. These are approximate values and can vary based on age, activity level, and individual metabolism.
⚡ Fast-Digesting Foods (15–45 minutes)
These foods are light, hydrating, and fiber-rich. They give you a quick boost and are great as pre-workout snacks or morning meals.
Food Average Digestion Time Benefits
Water 5–10 minutes Hydration, flushing toxins
Fruit Juice 15–30 minutes Vitamins, simple sugars
Watermelon 20 minutes High water, cooling
Apples 40 minutes Soluble fiber, gut-friendly
Pro Tip: Eat these foods before heavier meals to avoid fermentation or gas buildup.
⏱️ Moderate-Digesting Foods (45–90 minutes)
Perfect for keeping hunger at bay without making you feel sluggish, these foods are ideal for lunches or light dinners.
Food Digestion Time Notes
Eggs 30–45 minutes Great source of protein and easy on the gut
Carrots 50 minutes Packed with beta-carotene, very gentle
Potatoes 60 minutes Starchy, filling, ideal when baked
Cooked Vegetables 45–60 minutes Easier to digest than raw
Best Timing: Ideal before light physical activity, during work hours, or for early dinners.
🕒 Slow-Digesting Foods (2–6 hours)
These foods take a while to break down because they’re dense in protein, fats, or fiber. They’re best when you need long-term satiety, such as during long workdays or fasting windows.
Food Digestion Time Tip
Chicken 2–3 hours Lean protein, eat with light sides
Almonds 2–3 hours Nutritious but heavy, don’t over-snack
Cashews 2–6 hours Dense in healthy fat, eat sparingly
Red Meat 3–5 hours Tougher on digestion, not ideal for late dinners
Mind This: Avoid large portions of these close to bedtime or before workouts.
🍽️ Chapter 4: Sample Meal Plan Based on Digestion Time
To visualize how this plays out in real life, here’s a sample day built for optimal digestion:
🌞 Breakfast (Fast & Light)
- Chia seed pudding with watermelon cubes
- Herbal tea or lemon water
Digestion time: 30–45 minutes
Result: Hydration, energy, easy start for your gut
🕛 Lunch (Balanced)
- Grilled chicken breast
- Steamed carrots and quinoa
- Handful of almonds
Digestion time: 2–3 hours
Result: Sustained energy and satisfaction
🍃 Snack (Mid-Afternoon)
- Apple slices + almond butter
Digestion time: 40 mins to 1.5 hours
Result: Fuel without bloating
🌙 Dinner (Light)
- Lentil soup
- Baked sweet potato
- Mixed leafy greens with mint
Digestion time: ~1 hour
Result: Easy nighttime digestion
🧠 Chapter 5: Food Pairing Do’s and Don’ts
✅ Smart Combinations:
- Fruits → eaten alone or before meals
- Proteins + non-starchy veggies = great combo
- Water → 15–20 minutes before meals
🚫 Avoid These Combos:
- Fruit after meat or pasta = gas, bloating
- Too much liquid during meals = dilutes gastric acid
- Proteins + starches (e.g. steak + fries) = slower digestion, heaviness
Did You Know? The famous food-combining principle is practiced in several ancient dietary systems, including Ayurveda and traditional Chinese medicine.
📷 Chapter 6: Make It Visual—Digestive Charts, Trackers & Journals
Want to make food timing a habit? Here’s how:
- Create a visual digestion tracker: Draw your day in blocks of time, color-coded by how “light” or “heavy” meals are.
- Use food-plating apps: Combine plating aesthetics with macro-digestion planning.
- Photograph your meals daily: Not only does this help you stay accountable, it also trains your eye for balance and portion sizes.
Bonus: Photos of colorful, well-sequenced meals tend to go viral—especially when paired with tips like “eat your fruit before your coffee, not after.”
🌿 Chapter 7: Lifestyle Factors That Affect Digestion
Even the most digestion-aware meal can backfire if your lifestyle sabotages your stomach’s rhythm. Here’s what matters:
- Sleep Quality
Poor sleep slows digestion and encourages poor food timing the next day. - Stress
Cortisol affects stomach acid and gut motility. Stress-eating literally slows down digestion. - Hydration
Water is essential not only for digestion but for nutrient transport. - Movement
Light walking after meals improves motility and reduces gas buildup.
🌈 Chapter 8: The Emotional Side of Digestion
Yes, your gut truly feels your emotions. That “gut feeling” isn’t just a metaphor—your gut has its own nervous system (the enteric nervous system). This is why we feel butterflies, nausea, or heaviness based on our moods.
Practices like:
- Mindful eating (no screens, chew slowly)
- Gratitude journaling before meals
- Eating while calm rather than rushed
…all improve digestion indirectly but powerfully.
🧾 Chapter 9: A Digestive Reset Plan (3 Days)
Want to reboot your digestion? Here’s a quick reset program:
Day 1: Hydrate + Light
- Start with warm lemon water
- Focus on fruits + steamed veggies
- Avoid caffeine and red meats
Day 2: Add Proteins Wisely
- Eggs for breakfast
- Lentils and quinoa for lunch
- Chicken or tofu for dinner
- Ginger tea before bed
Day 3: Restore Balance
- Reintroduce healthy fats (avocado, olive oil)
- Keep water between meals only
- Avoid sugar and processed snacks
By day three, you’ll likely feel lighter, less bloated, and more in tune with your body’s natural rhythms.
✨ Final Thoughts: Eating With Time in Mind
Food is so much more than calories or trends